flowering plant.
Archaebacterium

Member of the prokaryotic domain Archaebacteria
Archean Eon

Eon in which life arose (3.8-2.5 bya).
Big Bang

Model for origin of universe.
Cenozoic Era
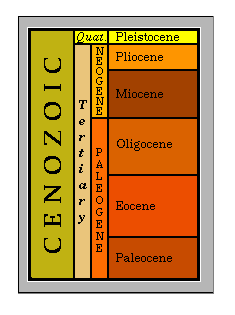
The present era (65 mya to present).
Crust
Outer zone of low-density rocks resting on the Earth's mantle.
Dinosaur

One of a fabulous group of reptiles that originated in the Triassic and became the dominant land vertebrates for 125 million years.
Ediacaran

One of the species with a highly flattened body that arose in the precambrian.
Endosymbiosis Theory
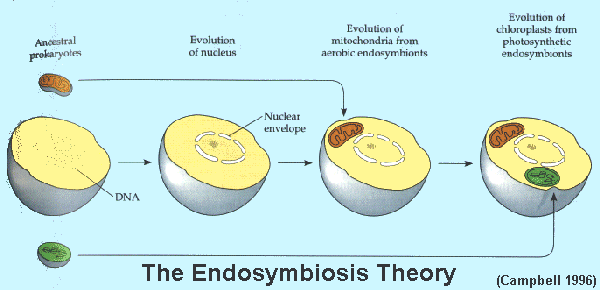
Continuing physical contact between two species, one of which lives and reproduces inside the other's body.
Eubacterium

Prokaryotic cell; has a nucleoid, but no nucleus, cytoplasm, or cell membrane; most have a cell wall, some encapsulated.
Eukaryotic cell
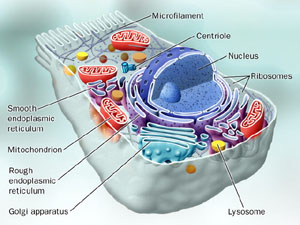
Cell having a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Global Broiling Hypothesis

Theory that an asteroid impact caused the K-T mass extinction by creating a colossal fireball, the debris from which raised global air temperature by thousands of degrees.
Gymnosperm

Type of vascular plant in which seeds form on exposed surfaces of reproductive structures (e.g., on cone scales).
K-T Asteroid impact theory

A huge asteroid hit Earth at the K-T boundary; last dinosaurs perished during the mass extinction.
Mantle

a tissue draped over the visceral mass. Of Earth, a zone of intermediatedensity rocks beneath the crust.
Mesozoic Era
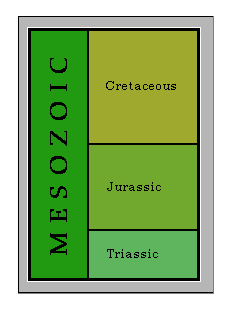
An era (240-65 mya) of spectacular expansion in the range of global diversity.
Paleozoic Era
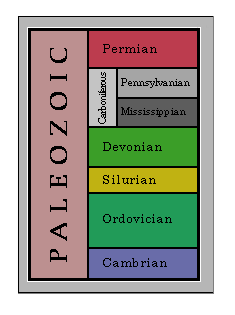
Era from Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, through the Permian (544 to 248 mya).
Prokaryotic cell
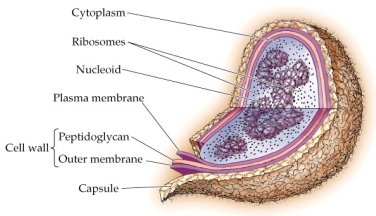
Archaebacterium or eubacterium; single-celled organism, most often walled; lacks the profusion of membranebound organelles observed in eukaryotic cells.
Proterozoic eon
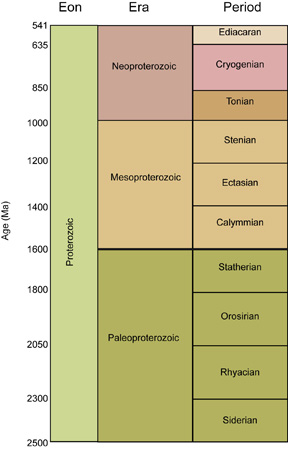
Period from 2.5 billion to 570 million years ago; period during which eukaryotic cells arose.
Protistan

Photoautotroph or heterotroph (or both) unlike bacteria; some like earliest eukaryotic cells. Has a nucleus, larger ribosomes, mitochondria, ER, Golgi bodies, chromosomes with numerous proteins, and cytoskeletal microtubules. Range in size from microscopic algae to giant kelps.
Proto cell

Hypothetic cell-like stage between chemical evolution and the first living cell.
RNA- world
One model for prebiotic evolution in which RNA was the template for protein synthesis before the evolution of DNA.
Stromatolite

Fossilized mats of shallow-water microbial communities, mainly cyanobacteria, from Archean to precambrian. Cell secretions blocked UV radiation but trapped sediments, and new mats grew on old ones; some are half a mile thick and hundreds of miles across.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario