Abortion
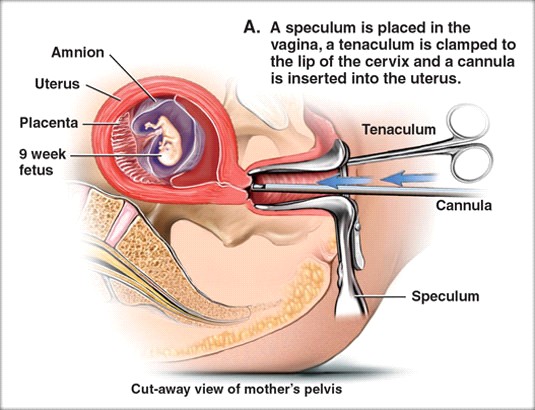
premature, spontaneous or induced expulsion of the embryo or fetus from uterus.
Aneuploidy
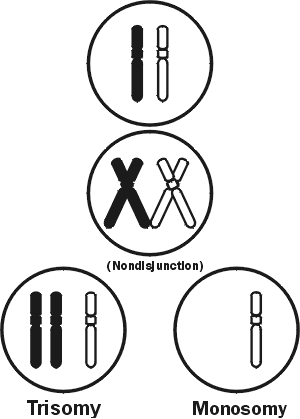
having one extra or less chromosome relative to the parental chromosome number.
Autosome

any chromosome of a type that is the same in males and females of the species.
Crossing Over

An interaction in which non sister chromatids of a pair of homologous chromosomes break and exchanges segments.
Deletion

Loss of a segement from a chromosome. At molecular level, loss of one to a few base pairs from a DNA molecule.
Disease

Outcome of infection when defenses aren´t mobilized fast enough and a pathogen´s activities interfere with normal body functions.
Double-blind study

different investigators independently collect, then compare data.
Duplication

Gene sequence repeated several to many hundreds or thousands of times.
Genetic Abnormality

A rare or less common version of a heritable trait.
Genetic Disorder

Any Inherited condition that causes mild to severe medical problems.
Genetic Recombination

Result of any process that puts new genetic information into a DNA molecule.
Homologous Chromosome
One of a pair of Chromosomes indentical in size, shape and gene sequenc, and that interact at meiosis.
In-Vitro Fertilization

Conception outside the body.
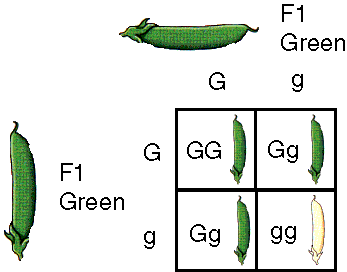
Independent Assortment

Mendelian Theory, each pair of homologous chromosomes are sorted before shipment to gametes independently of how the other pairs were sorted.
Inversion

Part of a chromosome that became oriented in reverse, with no molecular loss.
Karyotype
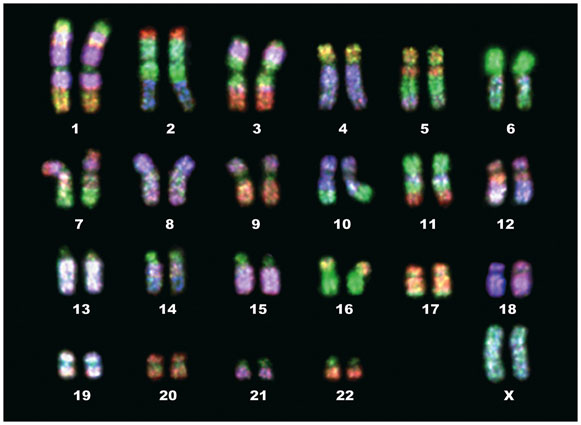
Preparation of methaphase chromosomes sorted by length, centromere location, other defining features.
Linkage Group

all genes on a chromosome.
Mosaicism

Cells of same type express genes differrently, so phenotypic differences emerge in same type of tissue.
Non-Disjunction

Failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis or mitosis.
Polyploidy

Having three or more of each type of chromosome in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell at interphase.
Reciprocal Cross

A paired cross. In the first cross, one parent displays the trait of interest. In the second, the other parent displays it.
Sex Chromosome

A chromosome with genes that affects sexual traits (XX females. XY males)
Syndrome

A set of symptoms that may not individually be a telling clue but collectively characterize a genetic disorder or disease.
Translocation

movement of a stretch of DNA to a new chromosomal location with no molecular loss.
X chromosome

Type of sex xhromosome, that becomes female.
Y chromosome

Type of sex chromosome, that become male.